Enabling Safe and Trusted AI Innovation
15 FEB 2026 11:12AM by PIB Delhi
Key Takeaways
- India adopts a principle-based AI governance framework anchored in seven Sutras to enable safe, trusted, and inclusive AI innovation across sectors.
- The guidelines recommends establishment of new national institutions including the AI Governance Group, Technology & Policy Expert Committee, and AI Safety Institute.
- AI governance guidelines prioritises innovation over restraint, positioning AI as a catalyst for inclusive growth, competitiveness, and the vision of Viksit Bharat 2047.
Introduction
Artificial Intelligence has emerged as the defining force of the Fifth Industrial Revolution, and India has articulated a clear, ambitious vision: to build the full AI stack, anchored in national priorities. India’s AI strategy is not confined to technological prowess alone; it is rooted in democratisation, scale, and inclusion. The objective is to ensure that AI is not concentrated in a handful of firms or geographies, but diffused across agriculture, healthcare, education, governance, manufacturing, and climate action. By focusing on “AI for All,” India seeks to combine sovereign capability with open innovation—leveraging public digital infrastructure, indigenous model development, and affordable compute to drive productivity and inclusive growth. This approach aligns AI development with the broader aspiration of Viksit Bharat 2047, positioning AI as a catalyst for economic transformation, social empowerment, and strategic autonomy.
India’s achievements reflect this deployment-first philosophy. Under the IndiaAI Mission, over 38,000 GPUs have been onboarded through a subsidised national compute facility. AIKosh now hosts more than 9,500 datasets and 273 sectoral models, strengthening indigenous model development. The National Supercomputing Mission has operationalised 40+ petaflop systems, including AIRAWAT and PARAM Siddhi-AI. On the capacity front, IndiaAI and FutureSkills initiatives are supporting 500 PhDs, 5,000 postgraduates, and 8,000 undergraduates, while 570 AI Data Labs and 27 IndiaAI labs across states are expanding grassroots innovation. With nearly 90 per cent of startups integrating AI in some form, India is embedding AI deeply into its innovation ecosystem.
The India AI Governance Guidelines, releasing in AI Impact Summit 2026, arrive at a critical juncture to consolidate these gains. Anchored in seven guiding sutras, the framework adopts a principle-based, techno-legal approach. By establishing new institutions such as the AI Governance Group, the Technology & Policy Expert Committee, and the AI Safety Institute, India is institutionalising a whole-of-government model that balances innovation with safeguards. The guidelines strengthen India’s ambition to lead not only in AI adoption and capability, but also in responsible, inclusive, and trusted AI governance globally.
India’s AI Governance Philosophy
India seeks to harness the transformative potential of artificial intelligence for inclusive development and global competitiveness, while addressing the risks it may pose to individuals and society. To advance this objective, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) constituted a drafting committee in July 2025 to develop a framework for AI governance in India. The Committee was mandated to draw on existing laws, review global developments, examine available literature, and incorporate public feedback in framing suitable governance guidelines.
Based on its deliberations, the Committee presented the AI governance framework in four parts. The first part sets out the seven sutras that ground India’s AI governance philosophy. The second part examines key issues and offers recommendations. The third part presents an action plan, and the fourth part provides practical guidelines for industry actors and regulators to ensure consistent and responsible implementation of the recommendations.
Part 1: Key Principles
The key principles of the AI Governance framework have been carefully designed to ensure cross-sectoral applicability and technology neutrality, enabling relevance across diverse use cases and stages of technological evolution. Together, these principles provide a flexible and future-ready foundation for responsible AI development and deployment.
|
|
| Trust is essential to support innovation, adoption, and progress, as well as risk mitigation. Without trust, the benefits of artificial intelligence will not be realised at scale. Trust must be embedded across the value chain – i.e. in the underlying technology, the organisations building these tools, the institutions responsible for supervision, and the trust that individuals will use these tools responsibly. Therefore, trust is the foundational principle that guides all AI development and deployment in India. | AI governance should place people at the centre. AI systems must be developed and deployed in ways that strengthen human agency and reflect societal values. From a governance standpoint, this requires that humans retain meaningful control over AI systems wherever possible, supported by effective human oversight. A people-first approach also emphasises capacity building, ethical protections, and safety considerations. |
|
|
| AI-led innovation is a pathway to achieving national goals, such as socio-economic development, global competitiveness, and resilience. Therefore, AI governance frameworks should actively encourage adoption and serve as a catalyst for impactful innovation. That said, innovation should be carried out responsibly and should aim to maximise overall benefit while reducing potential harm. All other things being equal, responsible innovation should be prioritised over cautionary restraint.
|
Promoting inclusive development is a central objective of India’s AI governance approach. AI systems should therefore be designed and evaluated to ensure fairness and to avoid bias or discrimination, particularly against marginalised communities. At the same time, AI should be actively used to advance inclusion while reducing risks of exclusion and unequal outcomes. |
|
|
| To ensure that India’s AI ecosystem progresses based on trust, AI developers and deployers should remain visible and accountable. Accountability should be clearly assigned based on the function performed, risk of harm, and due diligence conditions imposed. Accountability may be ensured through a variety of policy, technical, and market-led mechanisms.
|
Understandability is fundamental to building trust and should be a core design feature, not an afterthought. Though AI systems are probabilistic, they must have clear explanations and disclosures to help users and regulators understand how the system works, what it means for the user, and the likely outcomes intended by the entities deploying them, to the extent technically feasible. |
|
|
| AI systems should be designed with safeguards to minimise risks of harm and should be robust and resilient. These systems should have capabilities to detect anomalies and provide early warnings to limit harmful outcomes. AI development efforts should be environmentally responsible and resource-efficient, and the adoption of smaller, resource-efficient ‘lightweight’ models should be encouraged. | |
Together, these seven principles establish a coherent and balanced AI governance framework that enables innovation while safeguarding trust, equity, and accountability. They reflect India’s commitment to a people-centric, inclusive, and future-ready AI ecosystem. By aligning technological progress with societal values and developmental priorities, the framework provides a strong foundation for responsible AI adoption at scale.
Part 2: Key Issues and Recommendations
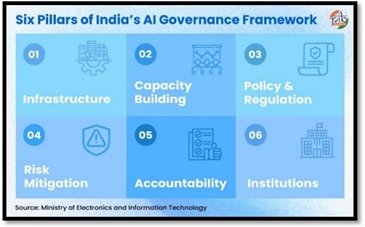
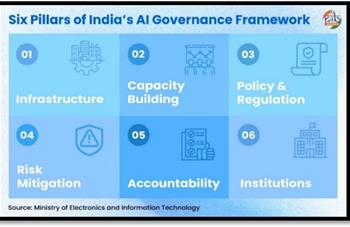
Using the seven principles or sutras as guidance, the Committee recommends an approach to AI governance that fosters innovation, adoption, and scientific progress, while proposing measures to mitigate the risks to individuals and communities. Effective governance includes not just regulation, but also other forms of policy engagement, including building capacity, infrastructure development, and institution building. The Committee has made recommendations across six pillars.
- Infrastructure
India’s AI governance framework seeks to promote innovation and large-scale adoption while mitigating societal risks. Under the India AI Mission, significant progress has been made in strengthening core infrastructure, including improved access to compute and datasets, development of foundational models, and deployment of AI applications, building on Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), enhanced data sharing, and safety testing. To sustain this momentum, continued investment in scalable infrastructure, equitable access to compute and data, and strong institutional capacity will be essential.
| Foundational AI Infrastructure Ecosystem | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
| What is Digital Public Infrastructure?
Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) refers to foundational digital systems that are accessible, secure, and interoperable, supporting essential public services. For example: Aadhaar, UPI, DigiLocker, Government e-Marketplace, UMANG, PM GatiShakti, among others. |
- Capacity Building
India has launched multiple AI capacity-building initiatives, including IndiaAI FutureSkills, FutureSkills PRIME, and higher education programmes, laying a strong foundation for an AI-ready workforce. As AI adoption accelerates, further scaling these efforts will help meet the demands of inclusive growth and broader access. Expanding AI exposure for small businesses and citizens, alongside strengthening technical capacity within the public sector, will support effective procurement, risk management, and responsible deployment of AI systems.
| Existing AI Human Resource & Innovation Capacity | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
- Policy & Regulation
The objective of the AI governance approach is to promote innovation, adoption, and technological progress while ensuring that risks to individuals and society are mitigated across the AI value chain. A review of the existing legal framework—comprising constitutional provisions, statutes, rules, regulations, and guidelines across domains such as information technology, data protection, intellectual property, competition, media, employment, consumer protection, and criminal law—indicates that many AI-related risks can be addressed under current laws.
At the same time, there is an urgent need for a comprehensive review of relevant laws to identify regulatory gaps relating to AI systems, including issues of classification and liability across the AI value chain, application of data protection principles to AI development, misuse of generative AI and challenges around content authentication and provenance, use of copyrighted material in AI training, and sector-specific risks in sensitive domains. While some of these issues are already under deliberation through inter-ministerial consultations, rulemaking, and expert committees, the rapid evolution of AI—including increasingly autonomous systems—poses challenges for regulatory frameworks to remain timely, coherent, and future-ready.
| Policy Foundations for Responsible AI | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
- Risk Mitigation
Risk mitigation is central to translating policy and regulatory principles into practical safeguards that prevent or reduce harm from AI systems. Given that AI systems are probabilistic, generative, adaptive, and agentic, they can introduce new risks or amplify existing ones across individuals, markets, and society. These risks include malicious uses such as AI-enabled misinformation and cyberattacks; bias and discrimination arising from inaccurate or unrepresentative data; transparency failures in the use of personal data; systemic risks linked to market concentration and geopolitical instability; loss of control over AI systems; and threats to national security and critical infrastructure.
Vulnerable groups face heightened exposure to these harms, particularly children—through exploitative recommendation systems—and women, who are disproportionately targeted by AI-generated deepfakes. Despite global and domestic efforts to classify and assess AI risks, India needs a profound context-specific risk assessment framework grounded in empirical evidence of real-world harms. The presence of a structured mechanism to systematically collect, analyse, and learn from AI-related incidents would equip policymakers, regulators, and institutions to anticipate emerging risks, design proportionate safeguards, and ensure accountability across sectors.
| Existing Risk Mitigation | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
- Accountability
Accountability is the backbone of AI governance, yet ensuring it in practice is challenging. Many AI-related risks can be addressed under existing laws, but their effectiveness depends on predictable and timely enforcement. Firms need meaningful pressure to comply, while regulators require visibility into organisational practices and the AI value chain. Current voluntary frameworks lack legal enforceability, and there is insufficient clarity on how liability should be attributed across developers, deployers, and end-users. Users often lack accessible and effective grievance redressal mechanisms, and transparency in AI system design, data flows, and organisational decision-making remains limited. AI systems’ probabilistic and adaptive nature may also generate unexpected outcomes, requiring a governance approach that balances enforcement with space for responsible innovation.
| Existing Accountability & Compliance Mechanisms | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
- Institutions
India’s AI governance framework would benefit from a coordinated “whole-of-government” approach to strengthen coherence and effectiveness. At present, responsibilities are distributed across multiple agencies, creating opportunities to enhance cross-sectoral coordination and strategic alignment. Establishing a permanent inter-agency mechanism could help oversee national AI strategy, assess emerging risks, guide implementation, and promote responsible innovation. While institutions such as MeitY, CERT-In, and the RBI play vital sector-specific roles, closer integration of technical expertise on AI policy, safety, and ethics would enable more robust risk assessment, guideline development, and informed engagement with industry, while ensuring alignment with India’s domestic and international strategic priorities.
| Existing Institutional Architecture for AI Governance | The Committee Further Recommends: |
|
|
| Whole-of-Government Approach
A coordinated framework where all relevant ministries, sectoral regulators, standards bodies, and public institutions collaborate to develop, implement, and oversee AI policy. This ensures alignment of strategies, avoids duplication, and promotes cohesive governance across sectors. |
Part 3: Action Plan
The Action Plan sets out a phased roadmap for the institutionalisation of AI governance, risk mitigation, and sustained adoption across sectors. It aligns short-term priorities with medium- and long-term reforms to translate governance principles into responsible, scalable, and inclusive outcomes, while remaining responsive to technological advances and emerging risks.
| Short-Term | Medium-Term | Long-Term |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
The AI Governance Guidelines are designed to deliver practical impact by strengthening institutions, managing risks effectively, and enabling responsible AI adoption, while fostering innovation, trust, and accountability across sectors. In the short term, coordinated institutions, India-specific risk frameworks, incident reporting mechanisms, voluntary compliance, and public awareness initiatives will build trust and governance capacity. Over the medium term, common standards, regulatory sandboxes, updated laws, and DPI integration will support safe innovation and smoother compliance. In the long term, India will establish a balanced, agile, and future-ready AI governance ecosystem with strong accountability, resilience to emerging risks, and enhanced global leadership in responsible AI governance.
Together, these outcomes will ensure that India’s AI ecosystem remains innovative, inclusive, and resilient, advancing technological progress while safeguarding societal interests.
Part 4: Practical Guidelines for Industry & Regulators
To enable consistent and responsible implementation of the AI Governance Framework, the Committee sets out practical guidance for industry participants involved in developing or deploying AI systems, alongside principles to guide policy formulation and enforcement by government agencies and sectoral regulators. These guidelines are intended to support innovation and adoption while ensuring that risks are addressed in a proportionate and context-appropriate manner.
| The Committee recommends that any person involved in developing or deploying AI systems in India should be guided by the following: | The Committee suggests the following principles to guide policy formulation and implementation by various agencies and sectoral regulators in their respective domains: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
These practical guidelines are intended to support consistent, lawful, and responsible development and deployment of AI systems in India. By clarifying expectations for industry and guiding proportionate policy action by regulators, they aim to enable innovation and adoption while strengthening trust, accountability, and effective risk management across sectors.
Conclusion
The India AI Governance Guidelines present a pragmatic, balanced, and agile framework that promotes safe, trusted, and responsible development and adoption of artificial intelligence in the country. Rooted in the seven guiding sutras — Trust is the Foundation, People First, Innovation over Restraint, Fairness & Equity, Accountability, Understandable by Design, and Safety, Resilience & Sustainability — the guidelines ensure that AI serves as an enabler for inclusive development, economic growth, and global competitiveness, while effectively addressing risks to individuals and society through proportionate, evidence-based measures.
Enabled by coordinated institutional leadership — including the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology as the nodal ministry, the AI Governance Group for strategic coordination, the Technology & Policy Expert Committee for expert advisory, the AI Safety Institute for technical validation and safety research, and sectoral regulators for domain-specific enforcement, this framework is designed to foster innovation, build public trust and position India as a responsible leader in the global AI ecosystem.
Through this structured and forward-looking architecture, India aims to realise the vision of AI for All, ensuring that the transformative potential of artificial intelligence contributes meaningfully to the national aspiration of Viksit Bharat by 2047, with benefits reaching every citizen in a safe, inclusive and sustainable manner.