Customs Integrated System will be rolled out in 2 years as a single, integrated and scalable platform
Fish catch by an Indian fishing vessel in Exclusive Economic Zone or on the High Seas will be made free of duty
The Government will roll out Customs Integrated System (CIS) in 2 years as a single, integrated and scalable platform for all the customs processes.
Announcing this while presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament today, Union Minister of Finance & Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that utilization of non-intrusive scanning with advanced imaging and AI technology for risk assessment will be expanded in a phased manner with the objective to scan every container across all the major ports.
The Union Minister further said that approvals required for cargo clearance from various Government agencies will be seamlessly processed through a single and interconnected digital window by the end of the financial year. She said that processes involved in clearance of food, drugs, plant, animal & wild life products, accounting for around 70 percent of interdicted cargo, will be operationalised on this system by April 2026 itself.
The Union Minister further said that for goods not having any compliance requirement, clearance will be done by Customs immediately after online registration is completed by the importer, subject to the payment of duty.
New export opportunities: The Finance Minister also said that the following measures will be taken to support Indian fishermen to fully harness the economic value of marine resources beyond our territorial waters:
a. Fish catch by an Indian fishing vessel in Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ) or on the High Seas will be made free of duty.
b. Landing of such fish on foreign port will be treated as export of goods.
She also said that safeguards will be put in place to prevent misuse during fish catch, transit and transshipment.
The Finance Minister further announced a complete removal of the current value cap of ₹10 lakh per consignment on courier exports to support aspirations of India’s small businesses, artisans and start-ups to access global markets through e-commerce. In addition, handling of rejected and returned consignments will be improved with effective use of technology for identifying such consignments, she added.
The Finance Minister further said that there are honest taxpayers who are willing to settle disputes by paying all their dues, but they get deterred due to negative connotation associated with penalty. They will now be able close cases by paying an additional amount in lieu of penalty, she added.
IMMUNITY FROM PROSECUTION FOR NON-DISCLOSURE OF NON IMMOVABLE FOREIGN ASSETS WITH AGGREGATE VALUE LESS THAN Rs 20 LAKH WITH RETROSPECTIVE EFFECT FROM 01.10.2024
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt Nirmala Sitharaman presented the Union Budget 2026-27 in the Parliament today. The Budget proposes set of Direct Tax proposals aiming at rationalizing penalty and prosecution.
The Finance Minister proposed to integrate assessment and penalty proceedings by way of a common order for both to avoid multiplicity of proceedings. There will be no interest liability on the taxpayer on the penalty amount for the period of appeal before the first appellate authority irrespective of the outcome of appeal process. Further, queantum of pre-payment is being reduced from 20 percent to 10 percent and will continue to be calculated only on core tax demand.
As an additional measure for reducing litigation, the Finance Minister proposed to allow taxpayers to update their returns even after reassessment proceedings have been initiated, at an additional 10 percent tax rate over and above the rate applicable for the relevant year. The assessing officer will then use only this updated return in his proceedings.
There is already a framework for immunity from penalty and prosecution in the cases of underreporting. The Finance Minister proposed to apply this framework of immunity to misreporting too. However, in such a case the taxpayer will need to pay 100 percent of the tax amount as an additional income tax over and above the tax and interest due.
Penalties for certain technical defaults such as failure to get accounts audited, non-furnishing of transfer pricing audit report and default in furnishing statement for financial transactions, are proposed to be converted into fee.
The Finance Minister proposed to rationalise prosecution framework under the Income Tax Act while maintaining a careful balance for deterrence in some serious offences.
Non-production of books of account and documents, and requirement of TDS payment, where payment is made in kind, are being decriminalised. Further, minor offences will attract fine only. The remaining prosecutions will be graded commensurate with the quantum of offence. They will entail only simple imprisonment, with maximum imprisonment reduced to two years, and power to courts to convert even those into fine.
There is no penalty presently for non-disclosure of non immovable foreign assets with aggregate value less than 20 lakh rupees. The Finance Minister proposed to also provide them with immunity from prosecution with retrospective effect from 1.10.2024.
THE INCOME TAX ACT,2025 TO COME INTO EFFECT FROM 1ST APRIL, 2026
TCS RATE FOR SCRAP AND MINERALS RATIONALIZED TO 2%
TCS FOR REMITTANCE UNDER LIBERALISED REMITTANCE SCHEME REDUCED FROM 5% TO 2% FOR EDUCATION AND MEDICAL TREATMENT
SHARES BUYBACK TO BE TAXED AS CAPITAL GAINS FOR ALL TYPES OF SHAREHOLDERS
Union Budget 2026-27 presented by the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman in the Parliament today emphasized the ‘Kartavya’ of sustaining the momentum of structural reforms. The Finance Minister proposed a slew of Direct tax reforms to simplify the tax regime and ensure better compliance by the citizens.
New Income Tax Act
The Income Tax Act, 2025 is slated to come into effect from 1st April 2026. The simplified Income Tax Rules and Forms will be notified in due course giving adequate time to taxpayers to acquaint themselves with its requirements. The forms have been redesigned for simpler understanding and compliance for ordinary citizens.
Tax administration
Smt. Sitharaman proposes to constitute a Joint Committee of Ministry of Corporate Affairs and Central Board of Direct Taxes for incorporating the requirements of Income Computation and Disclosure Standards (ICDS) in the Indian Accounting Standards (IndAS). Separate accounting requirement based on ICDS will be done away with from the tax year 2027-28.
To support the Prime Minister’s vision of home-grown accounting and advisory firms to become global leaders, the Budget proposes to rationalize the definition of accountant for the purposes of Safe Harbour Rules.
Other Tax proposals
- To curb the improper use of buyback by promoters, the budget proposes to tax buyback for all types of shareholders as Capital Gains. However, to disincentivize misuse of tax arbitrage, promoters will pay an additional buyback tax. This will make effective tax 22 percent for corporate promoters. For non corporate promoters the effective tax will be 30 percent.
- TCS rate for sellers of specific goods namely alcoholic liquor, scrap and minerals will be rationalized to 2 percent and that on tendu leaves will be reduced from 5 percent to 2 percent. TCS rate for Remittance under the Liberalised Remittance Scheme of an amount or aggregate of the amounts exceeding ten lakh rupees- (a) 2% for the purpose of education or medical treatment (b) 20% for the purpose of other than education or medical treatment
- Securities transaction tax (STT) proposed to be raised on Futures to 0.05 percent from present 0.02 percent. STT on options premium and exercise of options are both proposed to be raised to 0.15 percent from the present rate of 0.1 percent and 0.125 percent respectively.
- In continuance to simplified regime and lower tax rate for corporates, set-off of brought forward (Minimum Alternate tax) MAT credit is proposed to be allowed to companies only in the new regime to encourage companies to shift to the new regime. Set-off using available MAT credit is proposed to be allowed to an extent of 1/4th of the tax liability in the new regime.
- Ending further accumulation from 1st April, 2026, MAT is proposed to be made final tax. In line with this change, the rate of final tax will be reduced to 14 percent from the current MAT rate of 15 percent. The brought forward MAT credit of taxpayers accumulated till 31st March 2026, will continue to be available to them for set-off as above.
EASE OF LIVING BY DIRECT TAX REFORMS : UNION BUDGET 2026-2027
ANY INTEREST AWARDED BY THE MOTOR ACCIDENT CLAIMS TRIBUNAL TO A NATURAL PERSON TO BE EXEMPT FROM INCOME TAX
SCHEME FOR SMALL TAXPAYERS TO ENABLE OBTAINING A LOWER OR NIL DEDUCTION CERTIFICATE BY A RULE-BASED AUTOMATED PROCESS
TIME AVAILABLE FOR REVISING RETURNS EXTENDED FROM 31st DECEMBER TO 31st MARCH, FOR A NOMINAL FEE
ONE-TIME 6-MONTH FOREIGN ASSET DISCLOSURE SCHEME FOR SMALL TAXPAYERS TO DISCLOSE INCOME OR ASSETS
A range of proposals on Direct Taxes to ensure ‘Ease of living’ for taxpayers have been announced by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman during the Union Budget 2026-27 speech in Parliament today.
Ease of Living
The Budget proposes that any interest awarded by the Motor Accident Claims Tribunal to a natural person will be exempt from Income Tax, and any TDS on this account will be done away with. It proposes to reduce TCS rate on the sale of overseas tour program package from the current 5 percent and 20 percent to 2 percent without any stipulation of amount.
It aims to reduce TCS rate for pursuing education and for medical purposes under the Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS) from 5 percent to 2 percent. Supply of manpower services is proposed to be specifically brought within the ambit of payment to contractors for the purpose of TDS to avoid ambiguity. Thus, TDS on these services will be at the rate of either 1 percent or 2 percent only.

Ease for Taxpayers
A scheme for small taxpayers is proposed wherein a rule-based automated process will enable obtaining a lower or nil deduction certificate instead of filing an application with the assessing officer. For the ease of taxpayers holding securities in multiple companies, the budget proposes to enable depositories to accept Form 15G or Form 15H from the investor and provide it directly to various relevant companies. It extends time available for revising returns from 31st December to up to 31st March with the payment of a nominal fee.
Relaxed Tax return Timeline
The Budget proposes to stagger the timeline for filing of tax returns. Individuals with ITR 1 and ITR 2 returns will continue to file till 31st July and non-audit business cases or trusts are proposed to be allowed time till 31st August. TDS on the sale of immovable property by a non-resident is proposed to be deducted and deposited through resident buyer’s PAN based challan instead of requiring TAN.
Focus on Small Taxpayers
To address practical issues of small taxpayers like students, young professionals, tech employees, relocated NRIs, and such others, it aims to introduce a one-time 6-month foreign asset disclosure scheme for these taxpayers to disclose income or assets below a certain size. This scheme would be applicable for two categories of taxpayers namely, (A) who did not disclose their overseas income or asset and (B) who disclosed their overseas income and/or paid due tax, but could not declare the asset acquired.
For category (A), the limit of undisclosed income/asset is proposed to be up to 1 crore rupees. They need to pay 30 percent of Fair Market Value of asset or 30 percent of undisclosed income as tax and 30 percent as additional income tax in lieu of penalty and would thereby get immunity from prosecution. For category (B), asset value is proposed to be up to 5 crore rupees. Here, immunity from both penalty and prosecution will be available with the payment of fee of 1 lakh rupees.
EXEMPTION FROM MINIMUM ALTERNATE TAX (MAT) TO ALL NON-RESIDENTS WHO PAY TAX ON PRESUMPTIVE BASIS
TAX HOLIDAY TILL 2047 TO ANY FOREIGN COMPANY THAT PROVIDES CLOUD SERVICES TO CUSTOMERS GLOBALLY BY USING DATA CENTRE SERVICES FROM INDIA
SAFE HARBOUR OF 15 PERCENT ON COST IN CASE THE COMPANY PROVIDING DATA CENTRE SERVICES FROM INDIA IS A RELATED ENTITY
Recognising the need to enable critical infrastructure and boost investment in data centres,the Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman,while presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament today, proposed to provide tax holiday till 2047 to any foreign company that provides cloud services to customers globally by using data centre services from India. It will, however, need to provide services to Indian customers through an Indian reseller entity.
The Union Budget also proposes to provide a safe harbour of 15 percent on cost in case the company providing data centre services from India is a related entity.
To harness the efficiency of just-in-time logistics for electronic manufacturing, the Union Finance Ministerproposed in the budget to provide safe harbour to non-residents for component warehousing in a bonded warehouse at a profit margin of 2 percent of the invoice value. The resultant tax of about 0.7 percent will be much lower than in competing jurisdictions.
The Union Finance Minister in order to provide fillip to toll manufacturing in India, hasproposedin the Union budget 2026-27, to provide exemption from income tax for 5 years, to any non-resident whoprovides capital goods, equipment or tooling, to any toll manufacturer in a bonded zone.
The Budget proposals also provide exemption to global (non-India sourced) income of a non-resident expert, for a stay period of 5 years under notified schemes. This is intended to encourage vast pool of global talent to work in India for a longer period of time
The Union budget also proposes to provide exemption from Minimum Alternate Tax (MAT) to all non-residents who pay tax on presumptive basis.
UNION BUDGET 2026-27 PROPOSES SEVERAL INCENTIVES FOR COOPERATIVES
SUPPLY OF CATTLE FEED AND COTTON SEED PRODUCED BY A PRIMARY COOPERATIVE SOCIETY ALLOWED FOR DEDUCTION
INTER-COOPERATIVE SOCIETY DIVIDEND INCOME ALLOWED AS DEDUCTION UNDER THE NEW TAXATION REGIME
Union Budget 2026-27 has proposed several incentives for primary cooperative societies. Presenting the Budget in Parliament today, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman proposed to extend the deduction allowed to a primary cooperative society for supply of cattle feed and cotton seed produced by its members. Presently, deduction is allowed to a primary cooperative society engaged in supplying milk, oilseeds, fruits or vegetables raised or grown by its members.
The Finance Minister also proposed to allow inter-cooperative society dividend income as deduction under the new tax regime to the extent it is further distributed to its members.
As an additional measure to support National Cooperative Federations, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman further proposed to allow exemption for a period of 3 years, to dividend income received by a notified national co operative federation, on their investments made in companies up to 31.1.2026. This exemption would be allowed only for dividends further distributed to its member co-operatives.
THE UNION BUDGET 2026-27 PROPOSES HIGH-POWERED ‘EDUCATION TO EMPLOYMENT AND ENTERPRISE’ STANDING COMMITTEE TO RECOMMEND MEASURES ON THE SERVICES SECTOR
NEW NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF DESIGN TO BE ESTABLISHED IN THE EASTERN REGION OF INDIA THROUGH CHALLENGE ROUTE
CREATION OF 5 UNIVERSITY TOWNSHIPS IN THE VICINITY OF MAJOR INDUSTRIAL AND LOGISTIC CORRIDORS
1 GIRLS’ HOSTEL WILL BE ESTABLISHED IN EVERY DISTRICT THROUGH VGF/CAPITAL SUPPORT
4 TELESCOPE INFRASTRUCTURE FACILITIES TO BE SET UP OR UPGRADED TO PROMOTE ASTROPHYSICS AND ASTRONOMY
The Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, presented the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament today. The Union Budget proposes to set up a High-Powered ‘Education to Employment and Enterprise’ Standing Committee to recommend measures that focus on the Services Sector as a core driver of Viksit Bharat. This will make India a global leader in services, with a 10% global share by 2047. The Committee will prioritise areas to optimise the potential for growth, employment and exports. They will also assess the impact of emerging technologies, including AI, on jobs and skill requirements and propose measures thereof.

The Indian design industry is expanding rapidly and yet there is a shortage of Indian designers. The Union Budget proposes to establish, through challenge route, a new National Institute of Design to boost design education and development in the eastern region of India.
The Government will support States, through challenge route, in creating 5 University Townships in the vicinity of major industrial and logistic corridors. These planned academic zones will host multiple universities, colleges, research institutions, skill centres and residential complexes.

In the Higher Education STEM institutions, prolonged hours of study and laboratory work pose some challenges for girl students. The Union Budget proposes to establish 1 girls’ hostel in every district through VGF/capital support.
To promote Astrophysics and Astronomy via immersive experiences, 4 Telescope Infrastructure facilities will be set up or upgraded – the National Large Solar Telescope, the National Large Optical infrared Telescope, the Himalayan Chandra Telescope and the COSMOS 2 Planetariu
UNION BUDGET 2026-27 PROPOSES A SCHEME TO SUPPORT STATES IN ESTABLISHING FIVE REGIONAL MEDICAL HUBS TO PROMOTE MEDICAL TOURISM
NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF HOSPITALITY PROPOSED TO BE SET UP BY UPGRADING THE EXISTING NATIONAL COUNCIL FOR HOTEL MANAGEMENT AND CATERING TECHNOLOGY
PILOT SCHEME PROPOSED FOR UPSKILLING 10,000 GUIDES IN 20 ICONIC TOURIST SITES THROUGH A STANDARDIZED, HIGH-QUALITY 12-WEEK TRAINING COURSE
15 ARCHAEOLOGICAL SITES PROPOSED TO BE DEVELOPED; EXCAVATED LANDSCAPES WILL BE OPENED TO THE PUBLIC THROUGH CURATED WALKWAYS
SCHEME FOR DEVELOPMENT OF BUDDHIST CIRCUITS IN ARUNACHAL PRADESH, SIKKIM, ASSAM, MANIPUR, MIZORAM AND TRIPURA PROPOSED IN THE BUDGET
Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman while presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament said, “To promote India as a hub for medical tourism services, I propose to launch a Scheme to support States in establishing five Regional Medical Hubs, in partnership with the private sector.”
Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman stated that these Hubs will serve as integrated healthcare complexes that combine medical, educational and research facilities. She also added “They will have AYUSH Centres, Medical Value Tourism Facilitation Centres and infrastructure for diagnostics, post-care and rehabilitation. These Hubs will provide diverse job opportunities for health professionals including doctors and AHPs.”
Tourism
The Finance Minister said, “The Tourism sector has the potential to play a large role in employment generation, forex earnings and expanding the local economy.”

She said, “I propose to set up a National Institute of Hospitality by upgrading the existing National Council for Hotel Management and Catering Technology. It will function as a bridge between academia, industry and the Government.”
Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman proposed a pilot scheme for upskilling 10,000 guides in 20 iconic tourist sites through a standardized, high-quality 12-week training course in hybrid mode, in collaboration with an Indian Institute of Management.”
She also stated, “A National Destination Digital Knowledge Grid will be established to digitally document all places of significance—cultural, spiritual and heritage. This initiative will create a new ecosystem of jobs for local researchers, historians, content creators and technology partners.”
The Finance Minister said, “India has the potential and opportunity to offer world-class trekking and hiking experience. We will develop ecologically sustainable (i) Mountain trails in Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Jammu and Kashmir; Araku Valley in the Eastern Ghats and Podhigai Malai in the Western Ghats. (ii) Turtle Trails along key nesting sites in the coastal areas 14 of Odisha, Karnataka and Kerala; and (iii) Bird watching trails along the Pulikat lake in Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.”
She further said, “Under the visionary leadership of Honorable Prime Minister, we established the International Big Cat Alliance in 2024. This year, India is hosting the first ever Global Big Cat Summit, where heads of governments and ministers from 95 range countries will deliberate on collective strategies for conservation.”
Heritage and Culture Tourism
Speaking on the theme of Heritage and Culture Tourism, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman proposed to develop 15 archaeological sites including Lothal, Dholavira, Rakhigarhi, Adichanallur, Sarnath, Hastinapur, and Leh Palace into vibrant, experiential cultural destinations”.
She further said “Excavated landscapes will be opened to the public through curated walkways. Immersive storytelling skills and technologies will be introduced to help conservation labs, interpretation centres, and guides.”

Focus on the Purvodaya States and the North-Eastern Region
Speaking on Purvodaya Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman stated, “I propose the development of an integrated East Coast Industrial Corridor with a well-connected node at Durgapur, creation of 5 tourism destinations in the 5 Purvodaya States, and the provision of 4,000 e-buses.”
Speaking about Buddhist Sites in North-Eastern Region, she said that the North-Eastern Region is a civilizational confluence of Theravada and 18 Mahayana/Vajrayana traditions.
The Finance Minister further proposed to launch a Scheme for Development of Buddhist Circuits in Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Assam, Manipur, Mizoram and Tripura. The Scheme will cover preservation of temples and monasteries, pilgrimage interpretation centers, connectivity and pilgrim amenities.”
‘HIGH LEVEL COMMITTEE ON BANKING FOR VIKSIT BHARAT’ TO ALIGN FINANCIAL SECTOR WITH INDIA’S NEXT PHASE OF GROWTH: UNION BUDGET 2026-27
GOVERNMENT TO RESTRUCTURE THE POWER FINANCE CORPORATION AND RURAL ELECTRIFICATION CORPORATION TO ACHIEVE SCALE AND IMPROVE EFFICIENCY
UNION BUDGET PROPOSES A MARKET MAKING FRAMEWORK WITH SUITABLE ACCESS TO FUNDS AND DERIVATIVES ON CORPORATE BOND INDICES
TO ENCOURAGE THE ISSUANCE OF MUNICIPAL BONDS OF HIGHER VALUE, INCENTIVE OF ₹100 CRORE FOR A SINGLE BOND ISSUANCE OF MORE THAN ₹1000 CRORE
INDIVIDUAL PERSONS RESIDENT OUTSIDE INDIA TO BE PERMITTED TO INVEST IN EQUITY INSTRUMENTS OF LISTED INDIAN COMPANIES THROUGH THE PORTFOLIO INVESTMENT SCHEME
The Union Budget 2026-27 proposes to set up a ‘High Level Committee on Banking for Viksit Bharat’. Presenting the Union Budget in Parliament today, the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said that it will comprehensively review the financial sector and align it with India’s next phase of growth, while safeguarding financial stability, inclusion and consumer protection. Indian banking sector today is characterised by strong balance sheets, historic highs in profitability, improved asset quality and coverage exceeding 98% of villages in the country, the Union Budget noted.
The Union Budget proposes to restructure the Power Finance Corporation and Rural Electrification Corporation to achieve scale and improve efficiency in the Public Sector NBFCs. The vision for NBFCs for Viksit Bharat has been outlined with clear targets for credit disbursement and technology adoption.
Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman proposes a comprehensive review of the Foreign Exchange Management (Non-debt Instruments) Rules in the Union Budget to create a more contemporary, user-friendly framework for foreign investments consistent with India’s evolving economic priorities.

The Union Budget 2026-27 also proposes for a market making framework with suitable access to funds and derivatives on corporate bond indices along with a proposal for total return swaps on corporate bonds.
To encourage the issuance of municipal bonds of higher value by large cities, the Union Budget proposes an incentive of ₹100 crore for a single bond issuance of more than ₹1000 crore. The current scheme under AMRUT which incentivises issuances up to ₹200 crore, will also continue to support smaller and medium towns.
To enhance ease of doing business, Individual Persons Resident Outside India (PROI) will be permitted to invest in equity instruments of listed Indian companies through the Portfolio Investment Scheme. The Union Budget also proposes to increase the investment limit for an individual PROI under this scheme from 5% to 10%, with an overall investment limit for all individual PROIs to 24%, from the current 10%.
UNION BUDGET 2026-27 PROPOSES DEDICATED INITIATIVE FOR SPORTS GOODS TO PROMOTE MANUFACTURING, RESEARCH AND INNOVATION
INITIATIVE BUILDS ON INDIA’S POTENTIAL TO EMERGE AS A GLOBAL HUB FOR HIGH QUALITY, AFFORDABLE SPORTS GOODS
KHELO INDIA MISSION ANNOUNCED TO TRANSFORM THE SPORTS SECTOR OVER NEXT DECADE
KHELO INDIA MISSION TO TAKE FORWARD THE SYSTEMATIC NURTURING OF SPORTS TALENT SET IN MOTION THROUGH KHELO INDIA PROGRAMME
Leveraging India’s potential to emerge as a global hub for high quality, affordable sports goods, a dedicated initiative for sports goods is set to be launched in the country. This was stated by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, while presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament today.
The announcement on sports goods is centred on the first of the three kartavyas that form the pillars of this year’s Budget, namely, ‘to accelerate and sustain economic growth, by enhancing productivity and competitiveness, and building resilience to volatile global dynamics’. The aim of the sports goods initiative is to promote manufacturing, research and innovation, in both equipment design as well as material sciences.
The Union Budget puts forth another key proposal that seeks to strengthen India’s sporting ecosystem. In her Budget Speech, Smt. Sitharaman said, “The Sports Sector provides multiple means of employment, skilling and job opportunities. Taking forward the systematic nurturing of sports talent which is set in motion through the Khelo India programme, I propose to launch a Khelo India Mission to transform the Sports sector over the next decade.” This step aligns with the second kartavya outlined by the Budget, namely ‘to fulfil aspirations of our people and build their capacity, making them strong partners in India’s path to prosperity’.
As stated by the Finance Minister, the Khelo India Mission will facilitate the following:
- An integrated talent development pathway, supported by training centres at the foundational, intermediate and elite levels,
- Systematic development of coaches and support staff,
- Integration of sports science and technology,
- Competitions and leagues to promote sports culture and provide platforms; and,
- Development of sports infrastructure for training and competition.

INDIA ON TRACK TO REACH DEBT-TO-GDP RATIO OF 50±1 PERCENT BY 2030-31
FISCAL DEFICIT TO REMAIN AT4.4 PERCENT OF GDP AS PER RE 2025-26
FISCAL DEFICIT ESTIMATED TO BE 4.3 PERCENT OF GDP IN BE 2026-27
CAPITAL EXPENDITURE STANDS AT 11 LAKH CRORE OF TOTAL EXPENDITURE OF 49.6 LAKH CRORE AS PER RE 2025-26
CENTRE’S NET TAX RECEIPTS TO TOUCH 26.7 LAKH CRORE
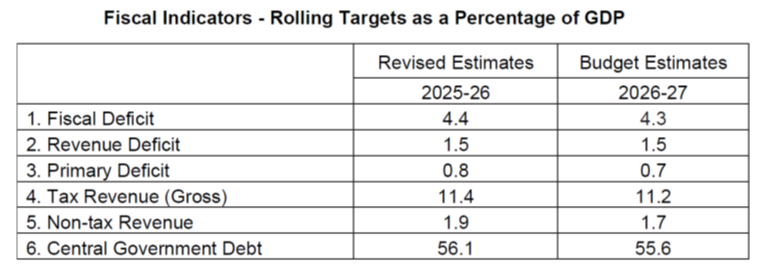
While presenting the Union Budget 2026-27in Parliament today, Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman stated, “Government has been delivering onfiscal commitments consistently without compromising on social needs.” In line with this, the debt-to-GDP ratio is estimated to be 55.6 percent of GDP in BE 2026-27, compared to 56.1 percent of GDP in RE 2025-26. A declining debt-to-GDP ratio will gradually free up resources for priority sectorexpenditure by reducing the outgo on interest payments.
Fiscal Deficit
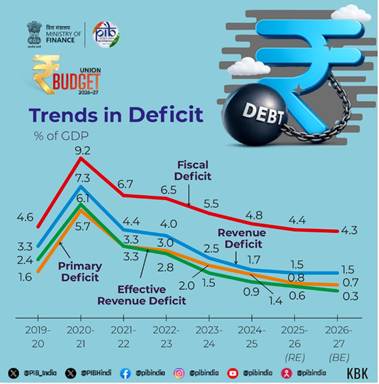
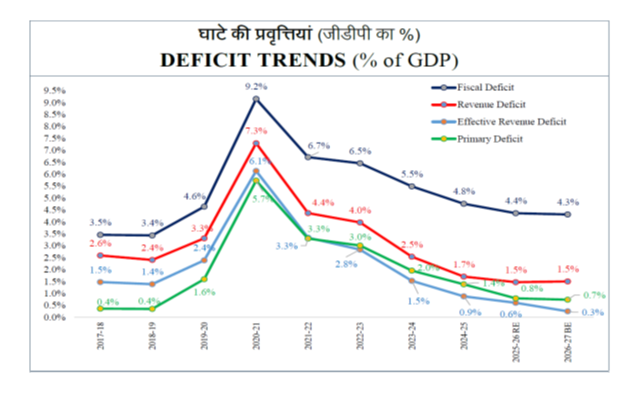
While speaking about Fiscal deficit, one of the main operational instruments for debt targeting, Smt. Sitharaman informedthe parliament tha commitment made in FY 2021-22 to reduce fiscal deficit below 4.5 percent of GDP by 2025-26 has been fulfilled. In RE 2025-26, the fiscal deficit has been estimated at par with BE of 2025-26 at 4.4 percent of GDP. In line with the new fiscal prudence path of debt consolidation, the fiscal deficit in BE 2026-27 is estimated to be 4.3 percent of GDP.”
Revised Estimates (RE) 2025-26.
The Finance Minister informedthat,“ The RE of the non-debt receipts are ₹34 lakh crore of which the Centre’s net tax receipts are ₹26.7 lakh crore. The Revised Estimate of the total expenditure is ₹49.6 lakh crore, of which the capital expenditure is about ₹11 lakh crore.”
Budget Estimates (BE) 2026-27
The Union Finance Minister stated that, “The non-debt receipts and the total expenditure are estimated as ₹36.5 lakh crore and ₹53.5 lakh crore respectively. The Centre’s net tax receipts are estimated at ₹28.7 lakh crore.”
Gross Market Borrowings
The Union Finance Ministersaid that “To finance the fiscal deficit, the net market borrowings from dated securities are estimated at ₹11.7 lakh crore. The balance financing is expected tocome from small savings and other sources. The gross market borrowings are estimated at ₹17.2 lakh crore.”
DIVYANG KAUSHAL YOJANA TO PROVIDE CUSTOMIZED TRAINING TO DIVYANGJAN IN IT, AVGC AND HOSPITALITY SECTORS
DIVYANG SAHARA YOJANA TO SET UP ASSISTIVE TECHNOLOGY MART AS MODERN RETAIL-STYLE CENTRES FOR DIVYANGJANS
The Union Minster of Finance and Corporate Affairs Smt Nirmala Sitharaman, while presenting the Union Budget 2026-2027 in the Parliament today said that our vision of Sabka Sath, Sabka Vikas, is to ensure that every family, community, region and sector has access to resources, amenities and opportunities for meaningful participation. To achieve this goal, the Finance Minister announced the following for divyangjan:
Divyangjan Kaushal Yojana: IT, AVGC sectors, Hospitality and Food and Beverages sectors offer task-oriented and process-driven roles, which are suitable for Divyangjans. This will ensure dignified livelihood opportunities through industry-relevant and customized training specific to each divyang group.
Divyang Sahara Yojana: Timely access to high-quality assistive devices for all eligible Divyangjans is a fundamental need. The budget proposes to (i) support the Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO) to scale up production of assistive devices, invest in R&D and AI integration, (ii) strengthen PM Divyasha Kendras and support setting up of Assistive Technology Marts as modern retail-style centres where Divyangjans and senior citizens can see, try and purchase assistive products.
GOVERNMENT ACCEPTS 16TH FINANCE COMMISSION’S RECOMMENDATION TO RETAIN VERTICAL SHARE OF DEVOLUTION AT 41 PERCENT
₹1.4 lakh cr. to BE GIVEN TO States as Finance Commission Grants for FY 2026-27
The Government has accepted the recommendation of the 16th Finance Commission to retain the vertical share of devolution at 41 percent.
Presenting the Union Budget 2026-27 in Parliament today, Union Minister of Finance & Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman said, “The Government has accepted the recommendation of the Commission to retain the vertical share of devolution at 41 percent. As recommended by the Commission, I have provided ₹1.4 lakh crore to the States for the FY 2026-27 as Finance Commission Grants. These include Rural and Urban Local Body and Disaster Management Grants.”
She further said that the Commission submitted its report to the President on 17th November 2025 and the Government is to lay the report along with the explanatory memorandum on the action taken report on the recommendations of the Commission in Parliament as mandated under Article 281 of the Constitution.
INDIA’S REAL GDP ESTIMATED TO GROW BY 7.4% IN FY 2025–26, WITH NOMINAL GDP GROWTH AT 8%
IN THE BUDGET FOR FY 2026-27, NOMINAL GDP IS PROJECTED TO GROW BY 10.0% OVER THE FIRST ADVANCE ESTIMATES OF FY 2025-26
SERVICE SECTOR REMAINS PRIMARY DRIVER OF GROWTH, EXPANDING BY 9.1%
TOTAL RESOURCES SHARED WITH STATES THROUGH THE FINANCE COMMISSION ROUTE ESTIMATED AT ₹16.56 LAKH CRORE IN BE 2026-27; INCLUDING TAX DEVOLUTION(₹15.26 LAKH CRORE) AND FC GRANTS(₹1.4 LAKH CRORE),
THE EFFECTIVE CAPITAL EXPENDITURE OF UNION GOVERNMENT IN FY 2026-27 ESTIMATED AT ₹17.15 LAKH CRORE, THAT IS 4.4% OF GDP
EFFECTIVE CAPITAL EXPENDITURE OF THE UNION GOVERNMENT INCLUDES GOI’S CAPITAL EXPENDITURE (₹12.22 LAKH CRORE) AND GRANTS-IN-AID TO STATES (₹4.93 LAKH CRORE) FOR CREATION OF CAPITAL ASSETS
CENTRAL GOVERNMENT DEBT TO GDP IS ESTIMATED AT 55.6% IN BE 2026-27, AS AGAINST 56.1% IN FY2025-26
PRIVATE FINAL CONSUMPTION EXPENDITURE (PFCE) IS PROJECTED TO GROW BY 7%, ACCOUNTING FOR 61.5% OF GDP – THE HIGHEST LEVEL SINCE FY12
GROSS FIXED CAPITAL FORMATION (GFCF) RISES BY 7.8% IN FY26
FISCAL DEFICIT FOR BE 2026-27 IS ESTIMATED AT 4.3%, WHILE FISCAL DEFICIT FOR RE 2025-26 IS 4.4%
REVENUE DEFICIT FOR BE 2026-27 IS ESTIMATED AT 1.5%; EFFECTIVE REVENUE DEFICIT FOR BE 2026-27 ESTIMATED AT 0.3%
GROSS TAX REVENUE IS ESTIMATED AT 11.2% OF GDP FOR BE 2026-27
THE CURRENT ACCOUNT DEFICIT DECLINED TO 0.8 PER CENT OF GDP IN H1 FY26 FROM 1.3 PER CENT IN H1 FY25.
INDIA’S TOTAL EXPORTS REACHED USD 825.3 BILLION IN FY25; DESPITE UNCERTAIN GLOBAL TARIFF SCENARIO
GROSS FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (FDI) INFLOWS WERE RECORDED AT USD 81.0 BILLION IN FY25
India’s growth outlook remains positive, supported by strong domestic demand, structural reforms, and a stable macroeconomic environment. The country received three sovereign rating upgrades during the year. Inflation outlook remains benign, as per Macroeconomic Framework Statement and Medium-term Fiscal Policy cum Fiscal Policy Strategy Statement laid by Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman on the table of the Parliament along with Budget for FY 2026-27. The document further adds that public investment, deregulation, labor market reforms, human capital investments, tax reforms, digital transformation, and the formalization of the economy are expected to drive the economy into a higher growth trajectory. Strong balance sheets in the corporate and financial sectors are also expected to drive a virtuous cycle of growth, fuelled by increased private-sector investment.
MACRO-ECONOMIC FRAMEWORK STATEMENT
Economic growth
As per the first advance estimates published by the National Statistics Office, India’s real GDP is estimated to grow by 7.4 per cent in FY 2025–26, with nominal GDP growth at 8 per cent. The services sector remains the primary growth driver, expanding by 9.1 per cent. Manufacturing and construction have grown by 7 per cent. Agriculture is estimated to grow at 3.1 per cent. In the Budget for FY 2026-27, nominal GDP is projected to grow by 10.0 per cent over the First Advance Estimates of FY 2025-26.
Consumption and Investment
Domestic demand continues to anchor growth. Private final consumption expenditure (PFCE) is projected to grow by 7 per cent, accounting for 61.5 per cent of GDP – the highest level since FY12. Government final consumption expenditure is also estimated to strongly rebound with a YoY growth of 5.2 per cent in FY26 as against 2.3 per cent in FY25. High-frequency indicators, such as UPI transactions, air and rail traffic, e-way bills, etc., reflect sustained momentum in both urban and rural consumption. Investment activity remains strong, with gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) rising by 7.8 per cent in FY26, higher than the previous year. Further, the share of GFCF has remained stable at around 30 per cent of GDP for the past three years.
External sector
India’s total exports (merchandise and services) reached USD 825.3 billion in FY25, with continued momentum in FY26. Despite tariffs imposed by the United States, merchandise exports grew by 2.4 per cent (April–December 2025), while services exports increased by 6.5 per cent. Merchandise imports for April-December 2025 increased by 5.9 per cent. Gross Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) inflows were recorded at USD 81.0 billion in FY25, and the momentum strengthened in FY26 with the highest inflow recorded in the first seven months of any financial year. The current account deficit declined to 0.8 per cent of GDP in H1 FY26 from 1.3 per cent in H1 FY25.
MEDIUM TERM FISCAL POLICY CUM STRATEGY STATEMENT
Fiscal Indicators
Union Budget 2026-27 has as its fiscal anchor the debt glide path indicated in Budget 2025-26 and Budget 2024-25 (regular) and is being presented against the backdrop of ongoing fiscal consolidation announced in FY 2021-22, which has provided a good foundation for making available the resources required to balance the development priorities without compromising on fiscal prudence. As announced in Budget 2021-22, the Government made true its intention of reaching a fiscal deficit below 4.5 per cent of GDP in FY 2025-26. Going ahead, it would be the Endeavour of the Government to adopt a fiscal stance that would put the Central Government debt on a declining path. Major fiscal indicators of the Union Government in the Revised Estimates (RE) of FY 2025-26 and the Budget Estimates (BE) of FY 2026-27 as a per cent of GDP, are summarized in the table below.
Receipts
In BE 2026-27, Gross Tax Revenue (GTR) is estimated at ₹44.04 lakh crore. It represents a growth of 8.0 per cent over RE 2025-26. Direct Taxes at ₹26.97 lakh crore are the major contributor to GTR (61.2 per cent of the GTR). Indirect taxes are estimated at ₹17.07 lakh crore. In BE 2026-27, the GTR to GDP ratio is estimated at 11.2 per cent. The Budget 2026-27 is also the first year of the award period of Sixteenth Finance Commission (SFC). SFC has recommended for retaining the share of devolution to the States at 41 per cent of divisible pool. The Tax Revenues (Net to Centre) are projected to be ₹28.67 lakh crore. In BE 2026-27, NTR of the Central Government is projected at ₹6.66 lakh crore. Revenue Receipts of the Union Government [comprising Tax Revenues (Net to Centre) and Non- Tax Revenues (NTR)], are estimated at ₹35.33 lakh crore. Revenue Receipt estimates assume a growth of 5.7 per cent over RE 2025-26.
Expenditure
The total expenditure of the Central Government in BE 2026-27 is projected to be ₹53.47 lakh crore (13.6 per cent of GDP) showing a growth of 7.7 per cent over RE 2025-26 of ₹49.65 lakh crore. The Budget for FY 2026-27 projects ₹12.22 lakh crore (3.1 per cent of GDP) towards capital expenditure. This includes capital support to States through SASCI (Special Assistance as Loan to States for Capital Expenditure) with an outlay of ₹2.0 lakh crore. Effective Capital Expenditure of the Union Government includes GoI’s capital expenditure and Grants-in-aid for creation of capital assets. Together, they constitute investments that enhance and upgrade productive capacity of the economy. In BE 2026-27, the allocation under Grants in- aid for creation of capital assets is projected at ₹4.93 lakh crore (or 1.3 per cent of GDP). Thus,
The effective capital expenditure in FY 2026-27 is estimated at ₹17.15 lakh crore (or 4.4 per cent of GDP).
Tax devolution and Finance Commission grants to the states
Based on recommendations of the Finance Commission (FC), the Union Government devolves taxes to States during the FC cycle. As mentioned previously, SFC recommended retaining States’ share at 41 per cent in the divisible pool, and this recommendation is accepted by the Government. In BE 2026-27, tax devolution to the States is estimated at ₹15.26 lakh crore compared to ₹13.93 lakh crore in RE 2025-26 which includes an additional amount of ₹9,084.02 crore on account of dues receivable by the Union Government from States under devolution from the previous years. Tax devolution to the States in BE 2026-27 is 3.9 per cent of GDP and ₹1.33 lakh crore more than tax devolution of RE 2025-26 (including past arrears). In BE 2026-27, the Finance Commission grants are estimated at ₹1.4 lakh crore. Thus, total resources shared, tax devolution and FC Grants, with States through the Finance Commission route are estimated at ₹16.56 lakh crore in BE 2026-27.

Fiscal policy strategy for 2026-27
The fiscal policy strategy for FY 2026-27 will continue to be guided by the debt glide path indicated in the Budget 2025-26. The medium-term aim to reach a debt to GDP ratio of 50±1 per cent by FY 2030-31, with the fiscal deficit acting as the operational target. In line with the above targets, it is estimated that Central Government debt to GDP ratio will be 55.6 per cent of GDP in BE 2026-27 with Fiscal Deficit target of 4.3 per cent of GDP. Other aspects of the fiscal strategy include support to economic growth through continued focus on capital expenditure, leaving adequate fiscal room to respond to global economic events and to ensure continued prosperity of the country in its journey towards Viksit Bharat. Other aspects include reforms in tax policy, expenditure policy, government borrowings, Lending and Investments.